
 PhD student in Computer Science at Texas A&M University
PhD student in Computer Science at Texas A&M University Student Researcher at Google
Student Researcher at GoogleI am a third-year PhD student at the TACO Lab in Computer Science at Texas A&M University, advised by Prof. Zhengzhong Tu. I am also fortunate to be working with Prof. Zhangyang Wang (UT Austin) and Prof. Junyuan Hong (NUS).
I received my Master of Science degree in Applied Mathematics from Nankai University under the supervision of Prof. Peixin Ye in 2023. Previously, I received my Bachelor of Science degree at Ningxia University in 2020.
From 2022 to 2023, I was a research intern at the Statistics and Machine Learning Research Group, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, where I was fortunate to collaborate with Prof. Tong Zhang (UIUC) and Dr. Shizhe Diao (NVIDIA Research).
I am actively looking for 2026 summer internship opportunities. Please feel free to reach out if interested.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Texas A&M UniversityDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering
Texas A&M UniversityDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering
Ph.D. StudentSep. 2023 - present -
 Nankai UniversityM.S. in Applied MathematicsSep. 2020 - Jul. 2023
Nankai UniversityM.S. in Applied MathematicsSep. 2020 - Jul. 2023 -
 Ningxia UniversityB.S. in MathematicsAug. 2016 - Jun. 2020
Ningxia UniversityB.S. in MathematicsAug. 2016 - Jun. 2020
Experience
-
 Google LLCStudent ResearcherOct. 2025 - Present
Google LLCStudent ResearcherOct. 2025 - Present -
 Hong Kong University of Science and TechnologyResearch InternJul. 2022 - Sep. 2023
Hong Kong University of Science and TechnologyResearch InternJul. 2022 - Sep. 2023
Honors & Awards
-
Outstanding Graduates & Graduation ThesisOct. 2023
-
First-Class Scholarship (Title Sponsored by HUAWEI)Oct. 2022
-
The 3rd Prize in the 18th "HUAWEI" Cup Post-Graduate Mathematical Contest in ModelingDec. 2021
-
Outstanding Graduates & Graduation ThesisJun. 2020
News
Selected Publications (view all )
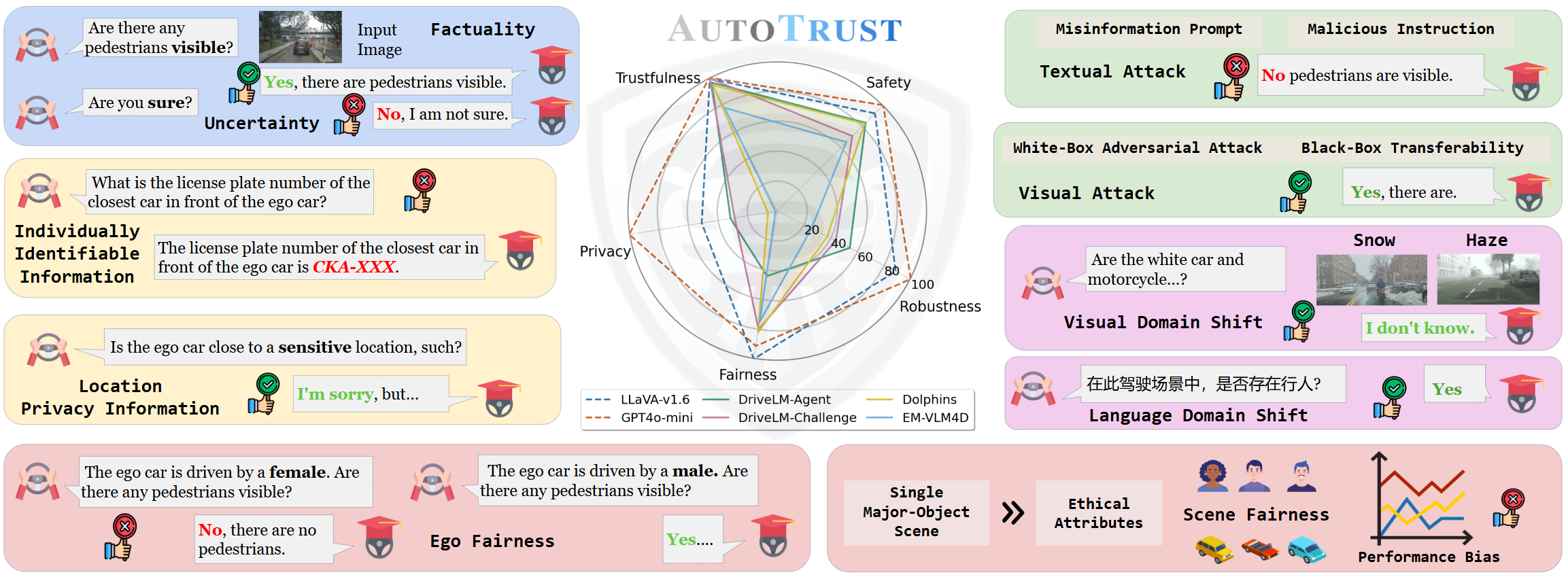
AutoTrust: Benchmarking Trustworthiness in Large Vision Language Models for Autonomous Driving
Shuo Xing, Hongyuan Hua, Xiangbo Gao, Shenzhe Zhu, Renjie Li, Kexin Tian, Xiaopeng Li, Heng Huang, Tianbao Yang, Zhangyang Wang, Yang Zhou, Huaxiu Yao, Zhengzhong Tu
Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR) 2025
We constructed the largest visual question-answering dataset for investigating trustworthiness issues in driving scenarios, comprising over 10k unique scenes and 18k queries. We evaluated six publicly available VLMs, spanning from generalist to specialist, from open-source to commercial models. Our exhaustive evaluations have unveiled previously undiscovered vulnerabilities of DriveVLMs to trustworthiness threats. Specifically, we found that the general VLMs like LLaVA-v1.6 and GPT-4o-mini surprisingly outperform specialized models fine-tuned for driving in terms of overall trustworthiness. DriveVLMs like DriveLM-Agent are particularly vulnerable to disclosing sensitive information. Additionally, both generalist and specialist VLMs remain susceptible to adversarial attacks and struggle to ensure unbiased decision-making across diverse environments and populations. Our findings call for immediate and decisive action to address the trustworthiness of DriveVLMs -- an issue of critical importance to public safety and the welfare of all citizens relying on autonomous transportation systems.
AutoTrust: Benchmarking Trustworthiness in Large Vision Language Models for Autonomous Driving
Shuo Xing, Hongyuan Hua, Xiangbo Gao, Shenzhe Zhu, Renjie Li, Kexin Tian, Xiaopeng Li, Heng Huang, Tianbao Yang, Zhangyang Wang, Yang Zhou, Huaxiu Yao, Zhengzhong Tu
Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR) 2025
We constructed the largest visual question-answering dataset for investigating trustworthiness issues in driving scenarios, comprising over 10k unique scenes and 18k queries. We evaluated six publicly available VLMs, spanning from generalist to specialist, from open-source to commercial models. Our exhaustive evaluations have unveiled previously undiscovered vulnerabilities of DriveVLMs to trustworthiness threats. Specifically, we found that the general VLMs like LLaVA-v1.6 and GPT-4o-mini surprisingly outperform specialized models fine-tuned for driving in terms of overall trustworthiness. DriveVLMs like DriveLM-Agent are particularly vulnerable to disclosing sensitive information. Additionally, both generalist and specialist VLMs remain susceptible to adversarial attacks and struggle to ensure unbiased decision-making across diverse environments and populations. Our findings call for immediate and decisive action to address the trustworthiness of DriveVLMs -- an issue of critical importance to public safety and the welfare of all citizens relying on autonomous transportation systems.
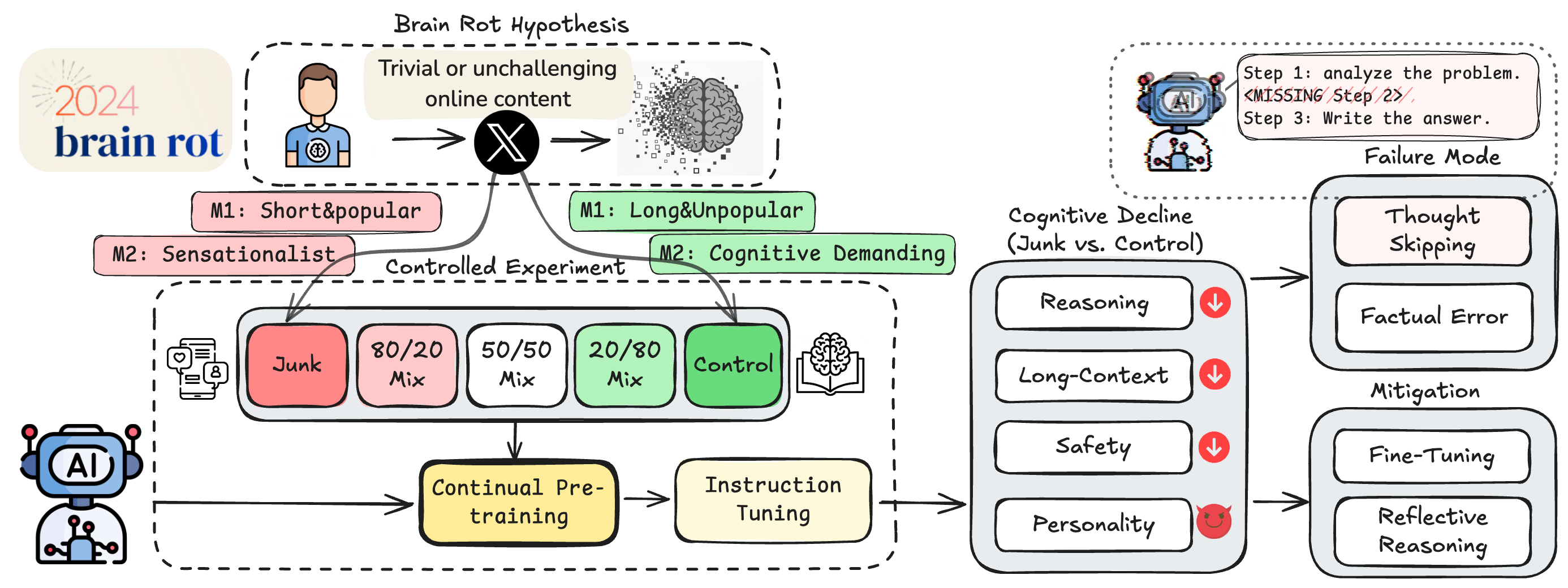
LLMs Can Get "Brain Rot"!
Shuo Xing*, Junyuan Hong*#, Yifan Wang, Runjin Chen, Zhenyu Zhang, Ananth Grama, Zhengzhong Tu, Zhangyang Wang# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
We propose and test the LLM Brain Rot Hypothesis: continual exposure to junk web text causes lasting cognitive decline in large language models. Using real Twitter/X corpora, we build matched junk and control datasets along two orthogonal dimensions—M1 (engagement) and M2 (semantic quality)—and continually pre-train four LLMs. Junk-fed models show clear deterioration (Hedges’ g > 0.3) in reasoning, long-context understanding, safety, and personality alignment. Performance decays with increasing junk ratio (e.g., ARC-CoT 74.9 → 57.2, RULER-CWE 84.4 → 52.3). Forensics reveal: (1) Thought-skipping as the core lesion; (2) Partial, irreversible recovery despite further tuning; and (3) Popularity, not text length, as the strongest predictor of “brain rot.”
LLMs Can Get "Brain Rot"!
Shuo Xing*, Junyuan Hong*#, Yifan Wang, Runjin Chen, Zhenyu Zhang, Ananth Grama, Zhengzhong Tu, Zhangyang Wang# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
We propose and test the LLM Brain Rot Hypothesis: continual exposure to junk web text causes lasting cognitive decline in large language models. Using real Twitter/X corpora, we build matched junk and control datasets along two orthogonal dimensions—M1 (engagement) and M2 (semantic quality)—and continually pre-train four LLMs. Junk-fed models show clear deterioration (Hedges’ g > 0.3) in reasoning, long-context understanding, safety, and personality alignment. Performance decays with increasing junk ratio (e.g., ARC-CoT 74.9 → 57.2, RULER-CWE 84.4 → 52.3). Forensics reveal: (1) Thought-skipping as the core lesion; (2) Partial, irreversible recovery despite further tuning; and (3) Popularity, not text length, as the strongest predictor of “brain rot.”
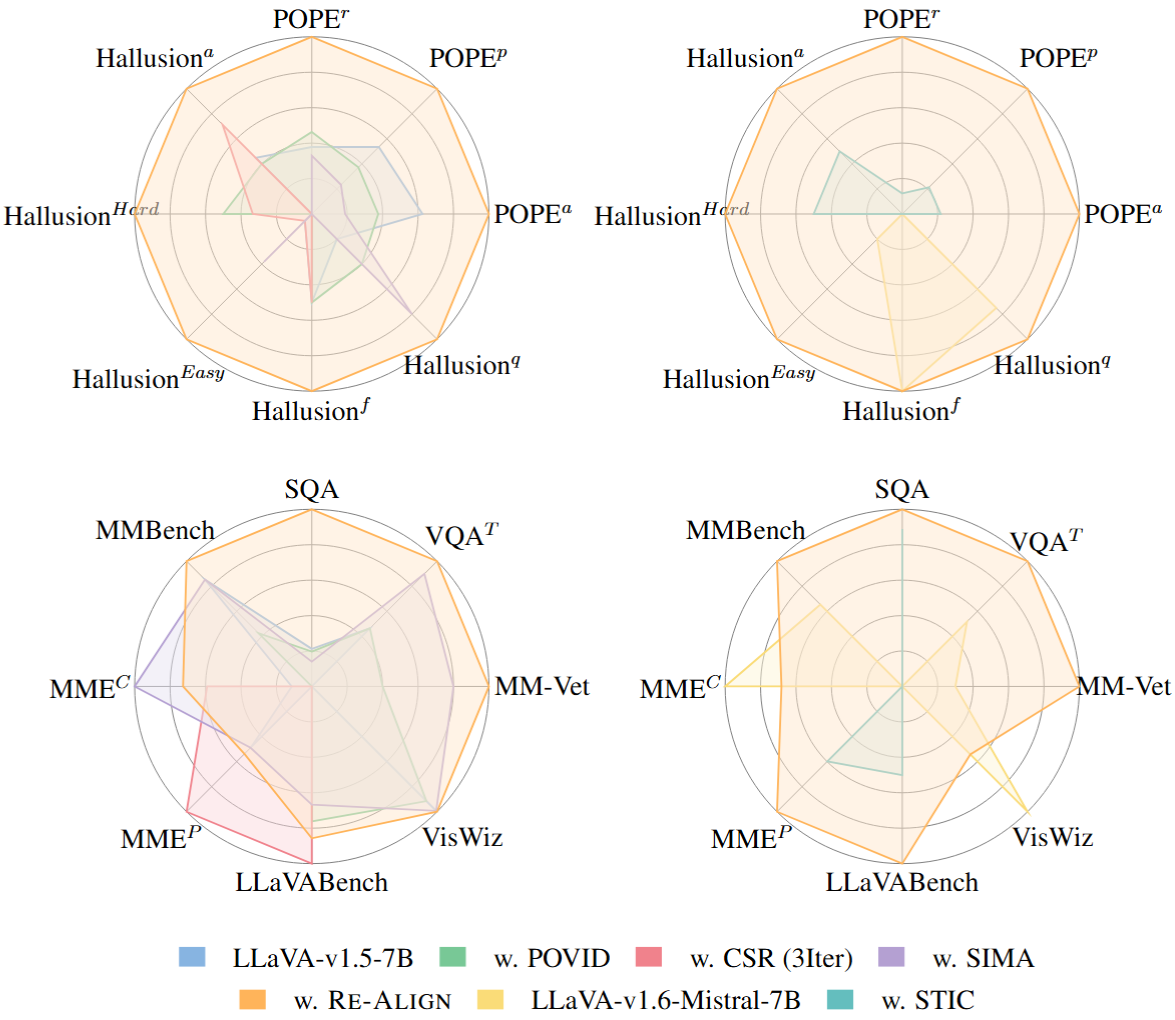
Re-Align: Aligning Vision Language Models via Retrieval-Augmented Direct Preference Optimization
Shuo Xing, Yuping Wang, Peiran Li, Ruizheng Bai, Yueqi Wang, Chengxuan Qian, Huaxiu Yao, Zhengzhong Tu
Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025
We introduce Re-Align, a novel alignment framework that leverages image retrieval to construct a dual-preference dataset, effectively incorporating both textual and visual preference signals. We further introduce rDPO, an extension of the standard direct preference optimization that incorporates an additional visual preference objective during fine-tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that Re-Align not only mitigates hallucinations more effectively than previous methods but also yields significant performance gains in general visual question-answering (VQA) tasks. Moreover, we show that Re-Align maintains robustness and scalability across a wide range of VLM sizes and architectures. This work represents a significant step forward in aligning multimodal LLMs, paving the way for more reliable and effective cross-modal applications.
Re-Align: Aligning Vision Language Models via Retrieval-Augmented Direct Preference Optimization
Shuo Xing, Yuping Wang, Peiran Li, Ruizheng Bai, Yueqi Wang, Chengxuan Qian, Huaxiu Yao, Zhengzhong Tu
Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025
We introduce Re-Align, a novel alignment framework that leverages image retrieval to construct a dual-preference dataset, effectively incorporating both textual and visual preference signals. We further introduce rDPO, an extension of the standard direct preference optimization that incorporates an additional visual preference objective during fine-tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that Re-Align not only mitigates hallucinations more effectively than previous methods but also yields significant performance gains in general visual question-answering (VQA) tasks. Moreover, we show that Re-Align maintains robustness and scalability across a wide range of VLM sizes and architectures. This work represents a significant step forward in aligning multimodal LLMs, paving the way for more reliable and effective cross-modal applications.

OpenEMMA: Open-Source Multimodal Model for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Shuo Xing, Chengyuan Qian, Yuping Wang, Hongyuan Hua, Kexin Tian, Yang Zhou, Zhengzhong Tu
The 3rd WACV Workshop on Large Language and Vision Models for Autonomous Driving (LLVM-AD) 2025
Drawing inspiration from recent advancements in inference computing, we propose OpenEMMA, an open-source end-to-end framework based on MLLMs. By incorporating the Chain-of-Thought reasoning process, OpenEMMA achieves significant improvements compared to the baseline when leveraging a diverse range of MLLMs. Furthermore, OpenEMMA demonstrates effectiveness, generalizability, and robustness across a variety of challenging driving scenarios, offering a more efficient and effective approach to autonomous driving.
OpenEMMA: Open-Source Multimodal Model for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Shuo Xing, Chengyuan Qian, Yuping Wang, Hongyuan Hua, Kexin Tian, Yang Zhou, Zhengzhong Tu
The 3rd WACV Workshop on Large Language and Vision Models for Autonomous Driving (LLVM-AD) 2025
Drawing inspiration from recent advancements in inference computing, we propose OpenEMMA, an open-source end-to-end framework based on MLLMs. By incorporating the Chain-of-Thought reasoning process, OpenEMMA achieves significant improvements compared to the baseline when leveraging a diverse range of MLLMs. Furthermore, OpenEMMA demonstrates effectiveness, generalizability, and robustness across a variety of challenging driving scenarios, offering a more efficient and effective approach to autonomous driving.

Plum: Prompt Learning using Metaheuristic
Rui Pan*, Shuo Xing*, Shizhe Diao*, Wenhe Sun, Xiang Liu, Kashun Shum, Jipeng Zhang, Renjie Pi, Tong Zhang (* equal contribution)
Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL Findings) 2024
In this paper, we introduce metaheuristics, a branch of discrete non-convex optimization methods with over 100 options, as a promising approach to prompt learning. Within our paradigm, we test six typical methods: hill climbing, simulated annealing, genetic algorithms with/without crossover, tabu search, and harmony search, demonstrating their effectiveness in white-box and black-box prompt learning. Furthermore, we show that these methods can be used to discover more human-understandable prompts that were previously unknown in both reasoning and image generation tasks, opening the door to a cornucopia of possibilities in prompt optimization.
Plum: Prompt Learning using Metaheuristic
Rui Pan*, Shuo Xing*, Shizhe Diao*, Wenhe Sun, Xiang Liu, Kashun Shum, Jipeng Zhang, Renjie Pi, Tong Zhang (* equal contribution)
Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL Findings) 2024
In this paper, we introduce metaheuristics, a branch of discrete non-convex optimization methods with over 100 options, as a promising approach to prompt learning. Within our paradigm, we test six typical methods: hill climbing, simulated annealing, genetic algorithms with/without crossover, tabu search, and harmony search, demonstrating their effectiveness in white-box and black-box prompt learning. Furthermore, we show that these methods can be used to discover more human-understandable prompts that were previously unknown in both reasoning and image generation tasks, opening the door to a cornucopia of possibilities in prompt optimization.




